| Journal of Neurology Research, ISSN 1923-2845 print, 1923-2853 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Neurol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.neurores.org |
Case Report
Volume 10, Number 4, August 2020, pages 136-139
Endovascular Reconstruction Utilizing Flow Diversion Stenting in a Patient With Bilateral Giant Cavernous Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysms
Keithan Sivakumara, Jaspreet Johala, Hussam Yacouba, b, c, Megan C. Learya
aLehigh Valley Health Network, Allentown, PA, USA
bMorsani College of Medicine, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA
cCorresponding Author: Hussam Yacoub, Lehigh Valley Health Network, 1250 S. Cedar Crest Blvd, Suite 405, Allentown, PA 18103, USA
Manuscript submitted May 2, 2020, accepted May 12, 2020, published online July 1, 2020
Short title: Flow Diversion Stenting for Giant ICA Aneurysms
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jnr593
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Bilateral giant cerebral aneurysms are exceedingly rare. Giant aneurysms of the internal carotid artery (ICA) carry a poor prognosis if untreated. Flow diversion is an endovascular technique whereby a device is placed in the parent blood vessel to divert blood flow away from the aneurysm and is an available treatment for giant aneurysms. A 69-year-old woman presented with progressive diplopia and was found to have bilateral ICA aneurysms. She had stenting of the left ICA aneurysm with improvement of her symptoms and no complications. Five years post procedure, she presented with recurrent diplopia and was found to have enlargement of the previously seen right-sided cavernous ICA aneurysm, which was treated with another flow diversion stent with no complications. Endoluminal reconstruction/flow diversion with Pipeline™ Embolization Device (PED) has emerged as an alternative to traditional endosaccular coiling and parent artery occlusion. We report a case of bilateral cavernous carotid giant aneurysms treated with flow diversion and demonstrate that flow diversion stenting using the PED is a safe and reliable treatment for bilateral giant ICA aneurysms. We encourage interventionists to consider this technique in patients with giant intracranial aneurysms.
Keywords: Cerebral aneurysms; Giant aneurysms; ICA aneurysms; Flow diversion; Stent coiling; Pipeline; PED
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Twenty percent of patients with cerebral aneurysms harbor multiple ones, often found bilaterally. Bilateral large or giant aneurysms are exceedingly rare. Large and giant aneurysms of the internal carotid artery (ICA) carry a poor prognosis if left untreated. Giant aneurysms, defined as those with a diameter greater than 25 mm, make up approximately 5% of all aneurysms [1]. A variety of treatment options have emerged, including open surgery, parent artery occlusion, and endovascular procedures, such as stent coiling or flow diversion [2-4].
Flow diversion is an endovascular technique whereby a device is placed in the parent blood vessel to divert blood flow away from an aneurysm. During a flow diversion procedure, a microcatheter is navigated past the aneurysm without entering the aneurysm itself. A flow diverting stent such as the Pipeline™ Embolization Device (PED) is then deployed across the aneurysm neck in the parent blood vessel where the aneurysm is present. This reduces blood flow to the aneurysm immediately, with complete closure typically occurring between 6 weeks and 6 months post procedure [5]. This closure is mediated at the cellular level by clusters of inflammatory cells that allow for initial flow diversion and is ultimately maintained by cells from the adjacent patent vessel [6].
In this report, we describe a rare case of bilateral giant intracranial ICA aneurysms treated successfully with a pipeline embolization device. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of bilateral ICA aneurysms treated using flow diversion.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A right-handed 69-year-old woman with a medical history of resected left trigeminal nerve hemangioma presented with progressive diplopia. She was found to have bilateral ICA aneurysms on neuroimaging. Figure 1a is a magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) scan showing a giant left cavernous ICA aneurysm, along with a smaller right cavernous carotid aneurysm. The same findings are seen on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with gadolinium in Figure 1b. She was enrolled in a treatment study known as Flow-Diversion Stent clinical trials at New York University Medical Center; she was the first patient enrolled in this study in the USA. She had significant improvement after stenting of the left ICA aneurysm with no immediate or delayed complications.
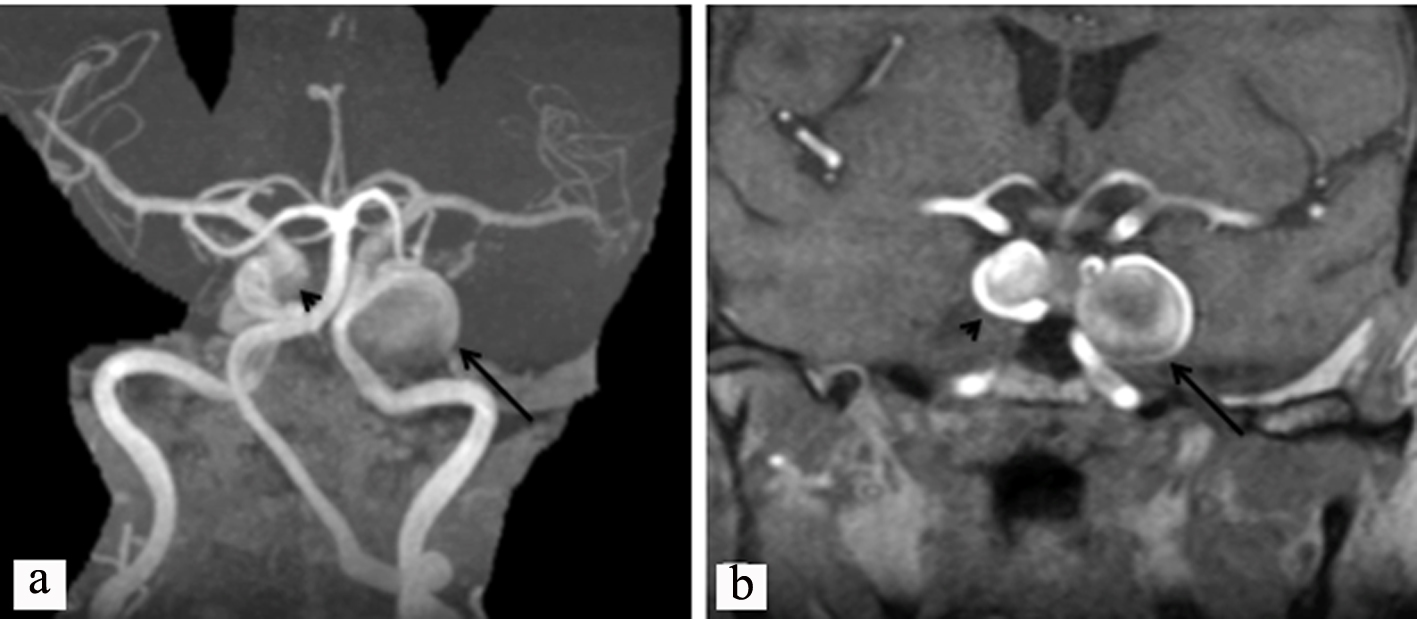 Click for large image | Figure 1. (a) Magnetic resonance angiography of the head showing a giant aneurysm of the left ICA (arrow) and a smaller aneurysm in the cavernous ICA on the right (arrow head). (b) Magnetic resonance imaging, T1, with gadolinium, showing a giant cavernous ICA aneurysm on the left (black arrow) and a smaller aneurysm in the cavernous ICA on the right (arrow head). ICA: internal carotid artery. |
Five years post procedure, she presented with recurrence of progressive diplopia. A follow-up MRI/MRA of the head revealed enlargement of the previously seen right-sided cavernous ICA aneurysm, now measuring 7 mm × 2.2 cm in its largest diameter. Figure 2a shows this enlarged right carotid aneurysm via cerebral angiography. The giant aneurysm was treated with another flow diversion stent with significant clinical improvement and no immediate or delayed complications. Successful flow diversion immediately after flow diversion is shown in Figure 2b, c, and is seen to be maintained 6 months after stent deployment in Figure 2d-f.
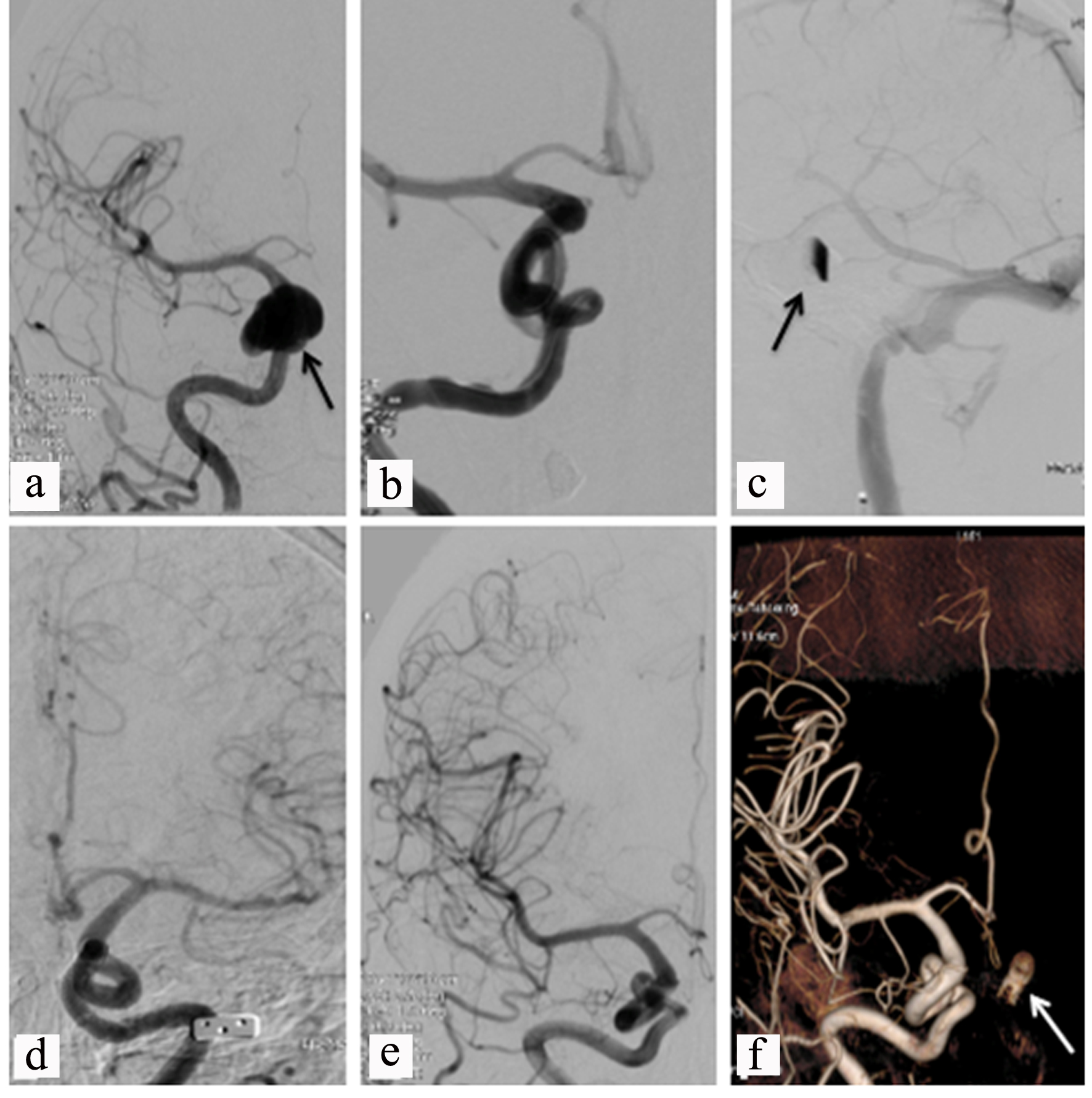 Click for large image | Figure 2. (a) Cerebral angiogram showing a giant right ICA aneurysm before treatment (black arrow). (b, c) Post-treatment with successful flow diversion (black arrow in (c)). (d-f) Six months post treatment, stable imaging and a left carotid stent (white arrow in (f)). ICA: internal carotid artery. |
Three months after the second procedure, the patient had no residual diplopia. Six months after treatment, a follow-up conventional cerebral angiogram demonstrated complete obliteration of the bilateral ICA aneurysms. To date, the patient remains stable with no recurrence of aneurysms or neurological symptoms.
| Discussion | ▴Top |
The presence of multiple intracranial saccular aneurysms is common, but the finding of bilateral large or giant aneurysms is exceedingly rare. One recent study examined the use of flow diversion for intracranial aneurysms and described its use in one case of bilateral fusiform aneurysms but did not comment on size or specifics of treatment [7]. A case series looking at 955 treated intracranial aneurysms in a 6-year period reported only 69 patients with large or giant aneurysms, of which none were bilateral [8].
Endoluminal reconstruction/flow diversion with PED has emerged as a viable, and often preferable, alternative to traditional endosaccular coiling and parent artery occlusion techniques [2, 9, 10]. The intent of this procedure is to treat large, fusiform, or wide-necked (> 4 mm) aneurysms that are more difficult to treat with conventional methods. The majority of aneurysms treated with flow diverting stents are usually unruptured and located in the anterior circulation. Flow diversion repair of aneurysms within the posterior circulation should only be done when no other treatment is optimal [11]. Repair of posterior circulation aneurysms with flow diversion is associated with higher mortality and perforator infarction than repairs of the anterior circulation [12].
A number of recent studies have examined the short-term and long-term outcomes following utilization of the flow diversion technique. One analysis found that use of the pipeline device in aneurysm treatment leads to complete aneurysmal occlusion in 12 months, with the exception of one case [13]. Another study performed a cost analysis of flow diversion versus endovascular coiling and concluded that for repair of large aneurysms with diameters greater than 12 mm, the flow diversion technique is more cost effective than coiling [14].
A recent case report presented the first occurrence of giant bilateral cavernous carotid aneurysms associated with polyarteritis nodosa, an inflammatory vasculitis, in a young patient [15]. Upon serial imaging and follow-up for 7 years, the enlarged aneurysm on the left was treated successfully with flow diversion with complete exclusion. No treatment of the right-sided aneurysm was reported [15]. In contrast, the giant aneurysms in our patient were not associated with an inflammatory condition and both were treated. Together, these case reports support the finding that flow diversion is an available, safe, and successful method of aneurysm treatment in this patient population.
One potential complication associated with the use of flow diversion stents is delayed aneurysm rupture. The risk of this complication can be lowered with the implementation of stent-assisted coils, which further reinforce the stent and provide additional protection for the repaired aneurysm [16]. A recent study used a computerized aneurysmal model to evaluate the fluid mechanics of the effect observed in the use of flow diversion stents. It concluded that the effect of the stents is limited to reducing flow velocity, and that the level of intra-aneurysmal pressure remains unchanged following intervention [16].
Conclusions
This case report is one of a few reporting bilateral cavernous giant aneurysms treated with flow diversion. Our case report also demonstrates that flow diversion stenting using the PED is a safe and reliable treatment for bilateral giant ICA aneurysms. We encourage interventionists to consider flow diversion as a treatment option in patients with giant intracranial aneurysms. Large cohort, multicenter studies are warranted to support our findings and evaluate the safety and outcome of this treatment.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Debra Goldberg, MA, for manuscript editing and formatting.
Financial Disclosure
No external funding was received in support of this work.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
KS, HY and JJ aided in writing the manuscript with MCL aiding in review and editing.
Data Availability
The authors declare that data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Abbreviations
ICA: internal carotid artery; PED: Pipeline™ Embolization Device; MRA: magnetic resonance angiography; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging
| References | ▴Top |
- Lv X, Jiang C, Li Y, Yang X, Zhang J, Wu Z. Treatment of giant intracranial aneurysms. Interv Neuroradiol. 2009;15(2):135-144.
doi pubmed - Becske T, Brinjikji W, Potts MB, Kallmes DF, Shapiro M, Moran CJ, Levy EI, et al. Long-term clinical and angiographic outcomes following pipeline embolization device treatment of complex internal carotid artery aneurysms: five-year results of the pipeline for uncoilable or failed aneurysms trial. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(1):40-48.
doi pubmed - Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Huston J, 3rd, Meissner I, Brown RD, Jr., Piepgras DG, Forbes GS, et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet. 2003;362(9378):103-110.
doi - Investigators UJ, Morita A, Kirino T, Hashi K, Aoki N, Fukuhara S, Hashimoto N, et al. The natural course of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in a Japanese cohort. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2474-2482.
doi pubmed - Seibert B, Tummala RP, Chow R, Faridar A, Mousavi SA, Divani AA. Intracranial aneurysms: review of current treatment options and outcomes. Front Neurol. 2011;2:45.
doi pubmed - Kadirvel R, Ding YH, Dai D, Rezek I, Lewis DA, Kallmes DF. Cellular mechanisms of aneurysm occlusion after treatment with a flow diverter. Radiology. 2014;270(2):394-399.
doi pubmed - Lubicz B, Collignon L, Raphaeli G, Pruvo JP, Bruneau M, De Witte O, Leclerc X. Flow-diverter stent for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a prospective study in 29 patients with 34 aneurysms. Stroke. 2010;41(10):2247-2253.
doi pubmed - Sluzewski M, Menovsky T, van Rooij WJ, Wijnalda D. Coiling of very large or giant cerebral aneurysms: long-term clinical and serial angiographic results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24(2):257-262.
- Becske T, Kallmes DF, Saatci I, McDougall CG, Szikora I, Lanzino G, Moran CJ, et al. Pipeline for uncoilable or failed aneurysms: results from a multicenter clinical trial. Radiology. 2013;267(3):858-868.
doi pubmed - Kallmes DF, Hanel R, Lopes D, Boccardi E, Bonafe A, Cekirge S, Fiorella D, et al. International retrospective study of the pipeline embolization device: a multicenter aneurysm treatment study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36(1):108-115.
doi pubmed - Briganti F, Leone G, Marseglia M, Mariniello G, Caranci F, Brunetti A, Maiuri F. Endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms using flow-diverter devices: A systematic review. Neuroradiol J. 2015;28(4):365-375.
doi pubmed - Wang CB, Shi WW, Zhang GX, Lu HC, Ma J. Flow diverter treatment of posterior circulation aneurysms. A meta-analysis. Neuroradiology. 2016;58(4):391-400.
doi pubmed - Lylyk P, Miranda C, Ceratto R, Ferrario A, Scrivano E, Luna HR, Berez AL, et al. Curative endovascular reconstruction of cerebral aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device: the Buenos Aires experience. Neurosurgery. 2009;64(4):632-642; discussion 642-633; quiz N636.
doi pubmed - Chiu AH, Nadarajah M, Wenderoth JD. Cost analysis of intracranial aneurysmal repair by endovascular coiling versus flow diversion: at what size should we use which method? J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2013;57(4):423-426.
doi pubmed - Martinez Santos J, Kaderali Z, Spears J, Rubin LA, Marotta TR. Flow diversion in vasculitic intracranial aneurysms? Repair of giant complex cavernous carotid aneurysm in polyarteritis nodosa using Pipeline embolization devices: first reported case. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016;8(7):e28.
doi pubmed - Shobayashi Y, Tateshima S, Kakizaki R, Sudo R, Tanishita K, Vinuela F. Intra-aneurysmal hemodynamic alterations by a self-expandable intracranial stent and flow diversion stent: high intra-aneurysmal pressure remains regardless of flow velocity reduction. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013;(Suppl 3):iii38-42.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Neurology Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.
