| Journal of Neurology Research, ISSN 1923-2845 print, 1923-2853 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Neurol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.neurores.org |
Case Report
Volume 7, Number 6, December 2017, pages 115-117
Eccrine Porocarcinoma of the Scalp: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Khalid M. Ashoura, c, Mustafa H. Alwalilya, Kamal B. Balkhoyora, Montasser A. Fodaa, Abdulrhman Saleh Dairia, Abdelazim L. Sadakaa, Sameen Shoaiba, Amal A. Hassanb
aDepartment of Neurosurgery, Al Noor Specialist Hospital, Holey Makkah, Saudi Arabia
bDepartment of Histopathology, Al Noor Specialist Hospital, Holey Makkah, Saudi Arabia
cCorresponding Author: Khalid Mohammad Ashour, Department of Neurosurgery, Al Noor Specialist Hospital, 56315, Al Azeezea, Holey Makkah 21955, Saudi Arabia
Manuscript submitted December 18, 2017, accepted December 27, 2017
Short title: Eccrine Porocarcinoma of the Scalp
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jnr464w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Eccrine porocarcinoma is an extremely rare malignant tumor that arises from the ductal part of sweat glands. It may present as asymptomatic nodule which may ulcerate or get infected and become itchy or painful. Porocarcinoma commonly arises in the legs and feet and rarely in the scalp. It can metastasize and it has a high rate of recurrence. Gross total surgical excision with safety margin is the main stone of management. We present a case of scalp porocarcinoma in an 83-year-old lady presenting with an infected scalp lesion. Gross total surgical excision with safety margin was done.
Keywords: Scalp tumors; Sweat glands; Porocarcinoma
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Eccrine porocarcinoma (EPC) is an extremely rare malignant tumor of skin appendages. It accounts for 0.005-0.01% of all skin tumors with potential for local destruction and metastasis [1, 2]. It is the malignant form of eccrine poroma, a common benign skin tumour of sweat glands [3]. Scalp is a rare site for EPC with a very few cases reported in the literature [1, 3]. EPC may develop de novo or as a result of malignant transformation of eccrine poroma [4]. Herein we present a rare case of an EPC of the scalp in an 83-year-old female, who had a long history of a scalp mass in the same site that was excised 10 years ago, with a literature review of other cases of EPC of the scalp.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
An 83-year-old female patient presented with scalp swelling that was gradually increasing in size over 6 months. The lesion was 5.6 × 5 cm, irregular firm swelling at the high bi-parietal region of the scalp. It was fixed to the scalp with slightly infected areas. The patient had a long history of scalp swelling almost at the same site but smaller which was totally excised 10 years prior to this admission. The nature of that lesion could not be confirmed. CT of brain showed extracranial moderately vascular soft tissue mass with fine calcifications with no bone erosion or intracranial extension (Fig. 1). Metastatic workup was negative.
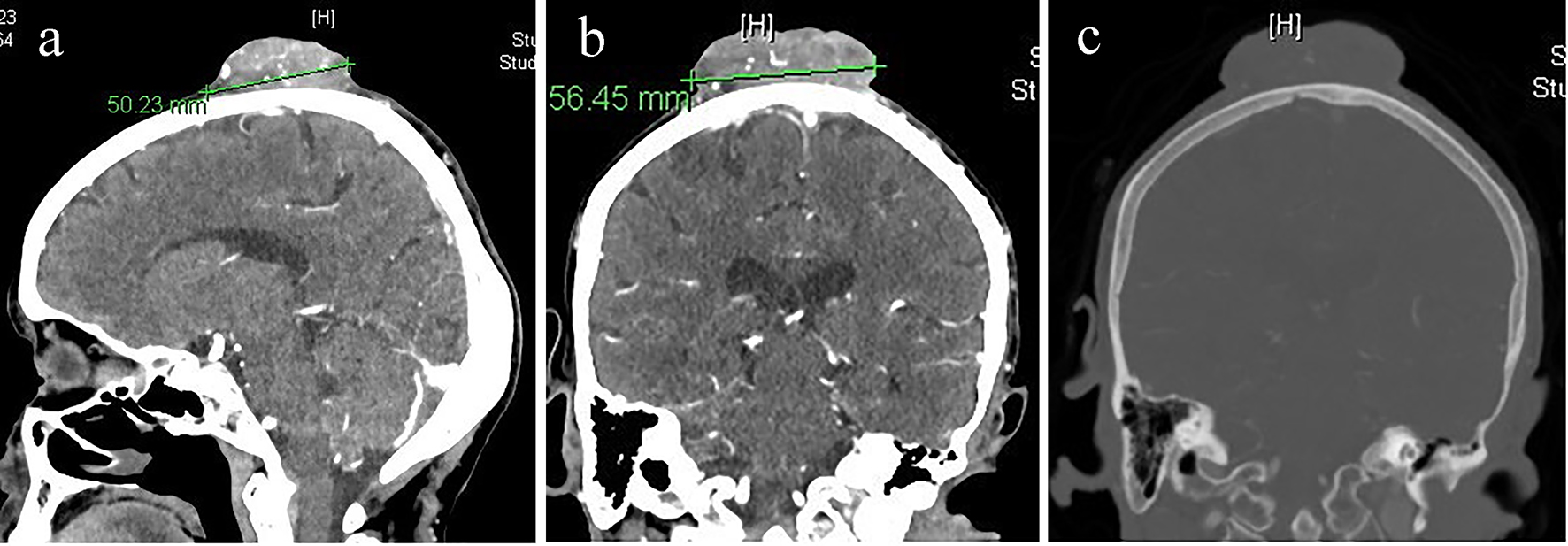 Click for large image | Figure 1. (a) CT of brain sagittal cut with IV contrast. (b) CT of brain coronal cut with IV contrast showing moderately vascular scalp mass. (c) CT of brain bone window showing no bone invasion or intracranial extension. |
Gross total excision of the lesion with safety margin of 1 cm all around was performed. The scalp defect was covered with a skin graft from the left thigh. Histopathological examination revealed sheets of neoplastic cells, arising from the epidermal layer and growing downward into the dermis. The tumor cells were composed of round to oval epithelial cells exhibiting nuclear atypia and central prominent nucleoli. Mitotic activities and apoptotic cells were plentiful. Central tumor necrosis was extensive (Fig. 2). The resection margins were free from tumor cells.
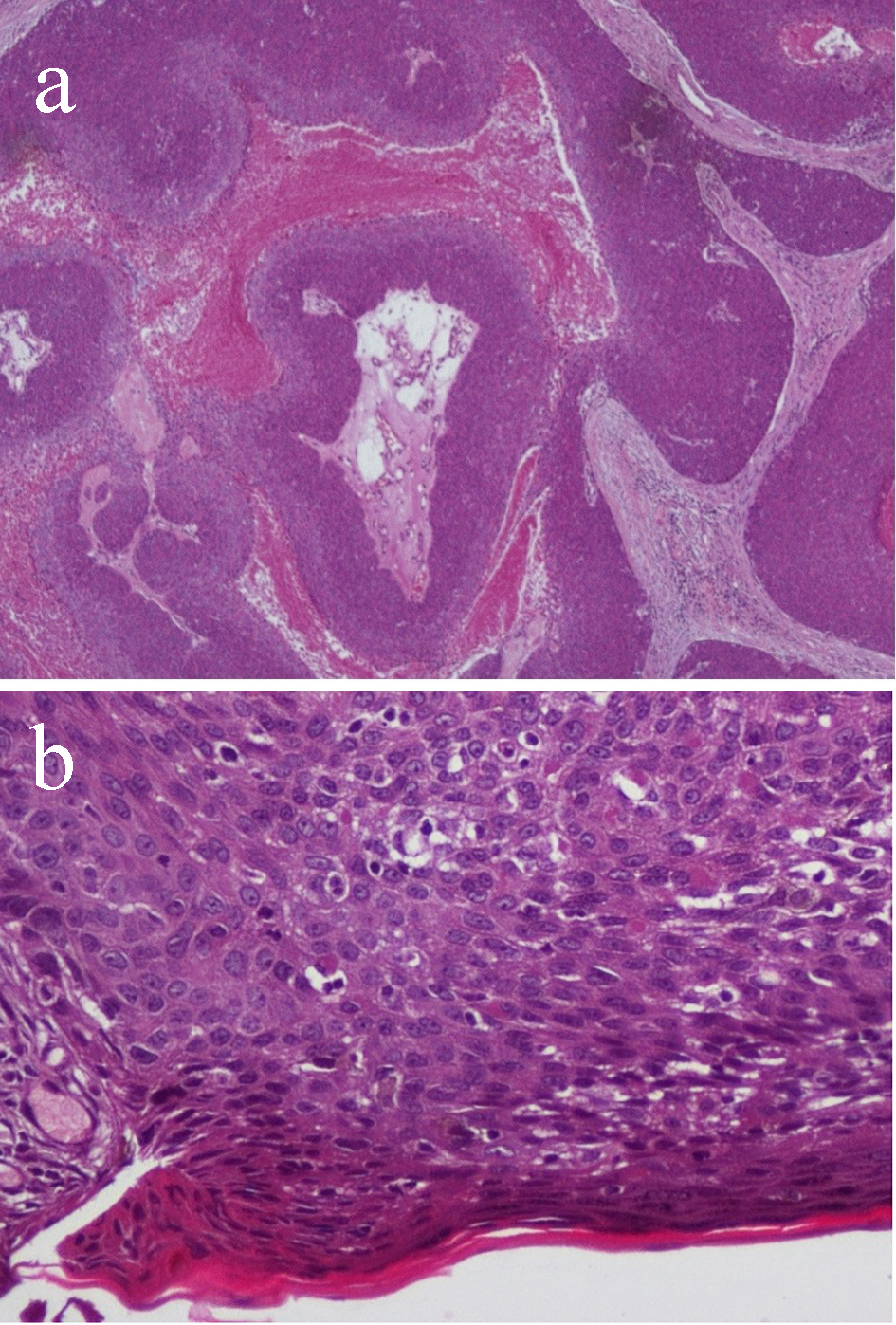 Click for large image | Figure 2. (a) Histopathology sections showing lobules of malignant cells separately by fibrovascular stroma (× 40). (b) Ulcerated epidermis with malignant poroid cells extending into the dermis. The malignant cells show numerous mitotic figures (× 200). |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Eccrine carcinoma was first reported by Pinkus and Mehregan in 1963 [5]. Mishima and Morioka later introduced the term (eccrine porocarcinoma) in 1969 [6].
It occurs equally in both genders and mainly in elderly at an average age of 68 [7].
The etiology of EPC is still unrecognized and its pathogenesis has not been clarified yet. Some risk factors have been reported as pre-existing lesions like “benign poroma after a long latency” [7]. Other risk factors include chronic exposure to the sun and immunocompromised status like HIV, diabetes mellitus and organ transplantation [8].
The clinical presentation of EPC is non-specific. The most common presentation is either as reddish mass or nodule that may ulcerate, become itchy and/or painful and may spontaneously bleed [9]. It commonly arises in the lower extremities “legs and feet”, trunk, head and neck and upper extremities [10, 11]. It rarely occurs in scalp, face, ear, eye lid and genitalia [2, 11]. In the scalp, it is commonly seen in occipital and frontoparietal regions [12, 13]. As it is exophytic tumor, bone involvement is rare [1]. Two cases of EPC with bone involvement were reported; one of them had intracranial extension and had manifestations of intracranial hypertension [12, 14]. To our knowledge, our case is the first one reported with the lesion in the high bi-parietal region of the scalp. It also has no bone involvement or intracranial extension. Distant metastases can be developed in the lung, breast, mediastinum, peritoneum, spine and liver [2].
The differential diagnosis includes many conditions like metastatic adenocarcinoma of the breast or lung, amelanotic melanoma, Paget’s disease, basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) [2, 9].
Because of the close histological resemblance of those lesions to the EPC, its rarity and its non-specific clinical features, the diagnosis of EPC only relies on its detection on histopathological examination [2, 9]. Histopathological criteria include: malignant neoplastic lesions extended from the epidermis to the dermis. These lesions are composed of large, basaloid and atypical neoplastic cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and some mitotic figures. Duct-like structures with eosinophilic cuticular borders are constant findings [15]. On the other hand, immunohistochemical features like positivity for carcinoembryonic antigen or epithelial membrane antigen help to confirm the diagnosis of difficult cases where histopathological findings are not conclusive [4].
Gross total surgical excision with safety margin is the main stone of management of EPC with cure rate of 70-80% [9, 15]. Lymph nodes dissection is to be considered in case of regional lymph node involvement [10]. Arslan et al recommended the use of adjuvant local radiotherapy to reduce local recurrence, especially when margins are close [16].
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are advised in metastatic lesions [7, 15].
Robson et al found that the prognosis of EPC is determined by histological factors that are predictive for poor prognosis. These are lymphovascular invasion, tumor margin status after resection, mitotic count (> 14/HPF) and tumor depth (> 7 mm) [17].
Conclusions
EPC of the scalp is a very rare malignant and lethal tumor. Given the non-specific clinical presentation in which it can be misdiagnosed with SCC, BCC and metastatic adenocarcinoma, the diagnosis of EPC must be based on histopathological features and this is essential because of its potential metastasis to distant organs. The main line of management is gross total surgical excision with safety margin. Adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy are used in cases of metastasis and to reduce local recurrence.
| References | ▴Top |
- Melgandi W, Benson R, Hakin A, Bhasker S. Porocarcinoma scalp with high risk features treated with surgery and adjuvant radiotherapy: A case report and review of literature. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2016;28(3):195-198.
doi pubmed - Jeon H, Smart C. An unusual case of porocarcinoma arising on the scalp of a 22-year-old woman. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015;37(3):237-239.
doi pubmed - Marone U, Caraco C, Anniciello AM, Di Monta G, Chiofalo MG, Di Cecilia ML, Mozzillo N. Metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma: report of a case and review of the literature. World J Surg Oncol. 2011;9:32.
doi pubmed - Vessels CM, Patel TS, Greenhaw BN, Shimek CM, Randall MB, Slominski A, Skinner RB. Scalp nodule on a middle-aged woman. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011;36(7):818-819.
doi pubmed - Pinkus H, Mehregan AH. Epidermotropic eccrine carcinoma. A case combining features of eccrine poroma and Paget’s dermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1963;88:597-606.
doi pubmed - Mishima Y, Morioka S. Oncogenic differentiation of the intraepidermal eccrine sweat duct: eccrine poroma, poroepithelioma and porocarcinoma. Dermatologica. 1969;138(4):238-250.
doi pubmed - Zeidan YH, Zauls AJ, Bilic M, Lentsch EJ, Sharma AK. Treatment of eccrine porocarcinoma with metastasis to the parotid gland using intensity-modulated radiation therapy: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:147.
doi pubmed - Luz Mde A, Ogata DC, Montenegro MF, Biasi LJ, Ribeiro LC. Eccrine porocarcinoma (malignant eccrine poroma): a series of eight challenging cases. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2010;65(7):739-742.
doi pubmed - Brown CW, Jr., Dy LC. Eccrine porocarcinoma. Dermatol Ther. 2008;21(6):433-438.
doi pubmed - Chang O, Elnawawi A, Rimpel B, Asarian A, Chaudhry N. Eccrine porocarcinoma of the lower extremity: a case report and review of literature. World J Surg Oncol. 2011;9:94.
doi pubmed - Masamatti SS, Narasimha A, Bhat A, Chowdappa V. Eccrine porocarcinoma of the scalp: a rare case report with review of literature. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(1):ED15-16.
doi - Ritter AM, Graham RS, Amaker B, Broaddus WC, Young HF. Intracranial extension of an eccrine porocarcinoma. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1999;90(1):138-140.
doi pubmed - Rana RE, Verma SS, Puri VA, Baliarsing AS. Sweat gland tumor (Eccrine Porocarcinoma) of scalp: A rare tumor. Indian J Plast Surg. 2005;38:51-53.
doi - Sigal R, Tordeur M, Avril MF, Spatz A, Vanel D. Eccrine porocarcinoma with intracerebral extension. Eur Radiol. 1997;7(4):573-575.
doi pubmed - Kurashige Y, Minemura T, Nagatani T. Eccrine porocarcinoma: clinical and pathological report of eight cases. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013;5(3):259-266.
doi pubmed - Arslan E, Unal S, Cinel L, Demirkan F, Cin I. Malignant eccrine spiradenoma occurring on a traumatized area. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;110(1):365-367.
doi pubmed - Robson A, Greene J, Ansari N, Kim B, Seed PT, McKee PH, Calonje E. Eccrine porocarcinoma (malignant eccrine poroma): a clinicopathologic study of 69 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001;25(6):710-720.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Neurology Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.
