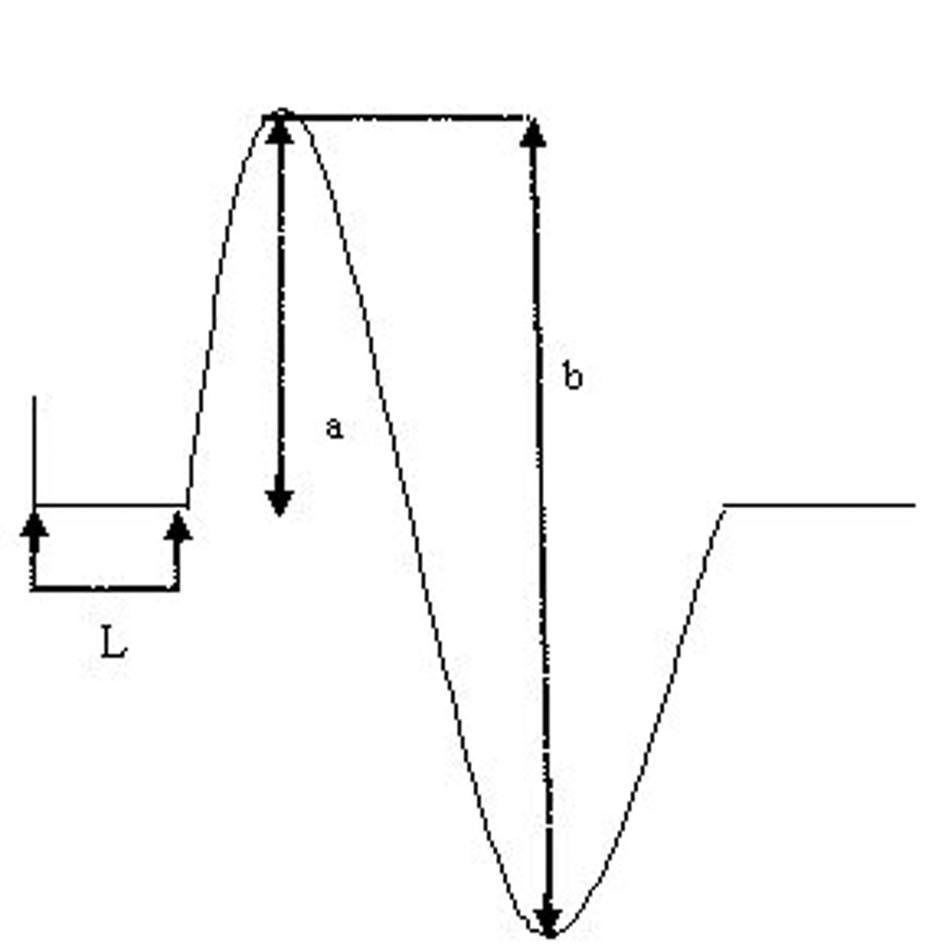
Figure 1. Measurement of CMAP latency and amplitude. L =latency; c = base to peak amplitude; b = peak to peak amplitude.
| Journal of Neurology Research, ISSN 1923-2845 print, 1923-2853 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Neurol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.neurores.org |
Original Article
Volume 1, Number 5, December 2011, pages 210-214
Delayed Axillary Nerve Motor Conduction Latency and Reduced CMAP Amplitudes in the Paretic Limbs of Patients With a Cerebrovascular Episode
Figures

Tables
| Mean | Standard deviation | Median | Inter quartile range | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 58 | 4.1 | 59 | 46 - 65 |
| Stroke duration (days) | 57.9 | 11.39 | 56 | 44 - 76 |
| Muscle power in shoulder abductors (MRC grade) | 3 | 1.37 | - | - |
| Paretic limb | Non-paretic limb | P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean (SD) | Median (Range) | Mean (SD) | Median (Range) | |
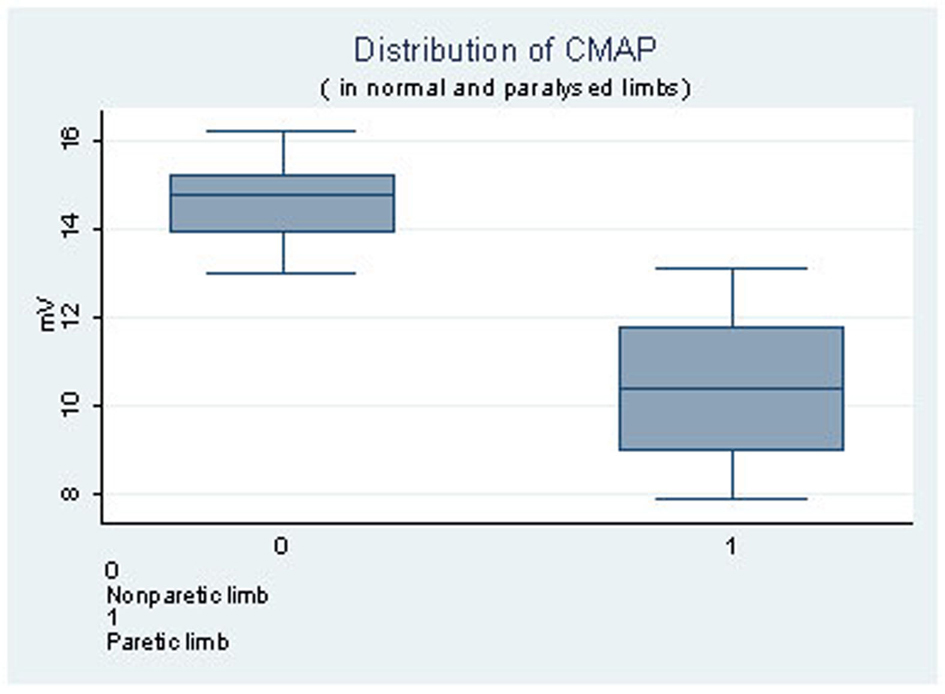
| CMAP | 10.51 (0.90) | 14.8 (13 - 16.2) | 14.63 (1.64) | 10.4 (7.9 - 13.1) | < 0.001 |
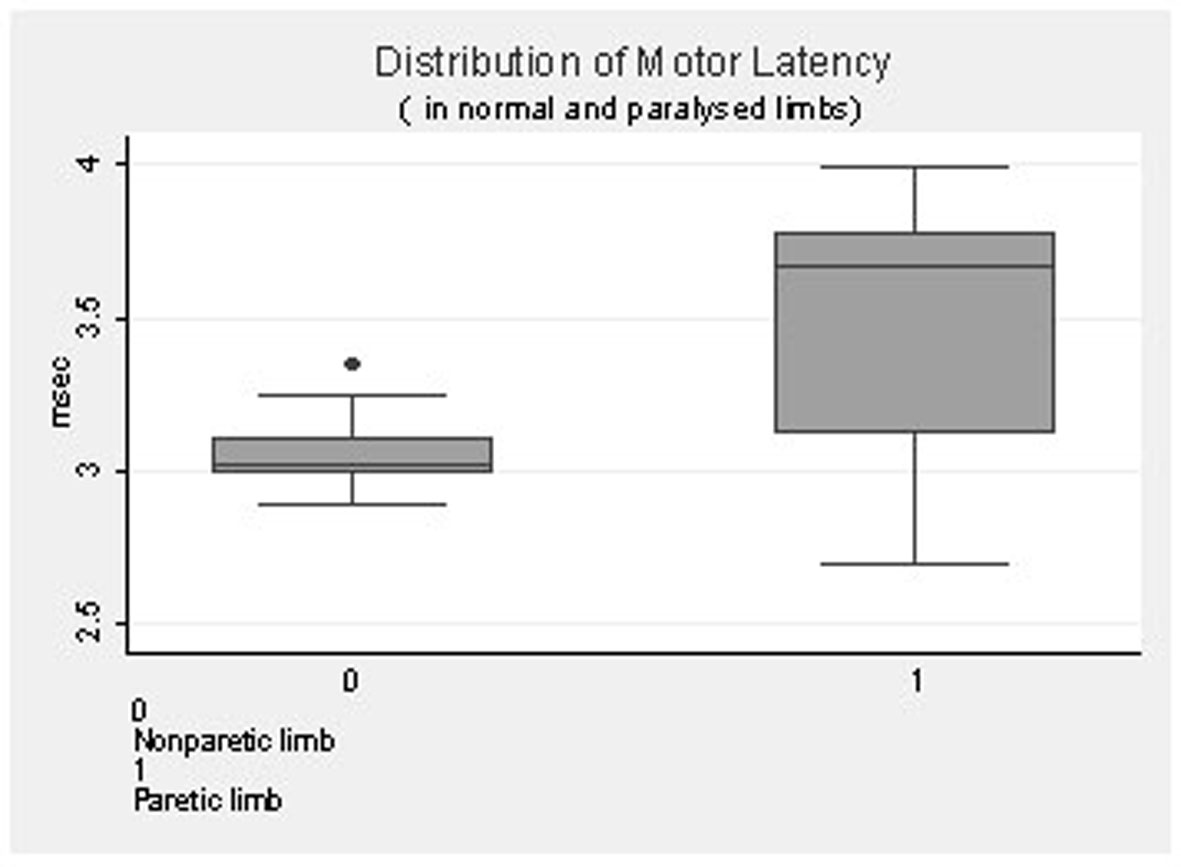
| CML | 3.54 (0.38) | 3.67 (2.69 - 3.9) | 3.05 (0.21) | 3.02 (2.8 - 3.3) | < 0.001 |