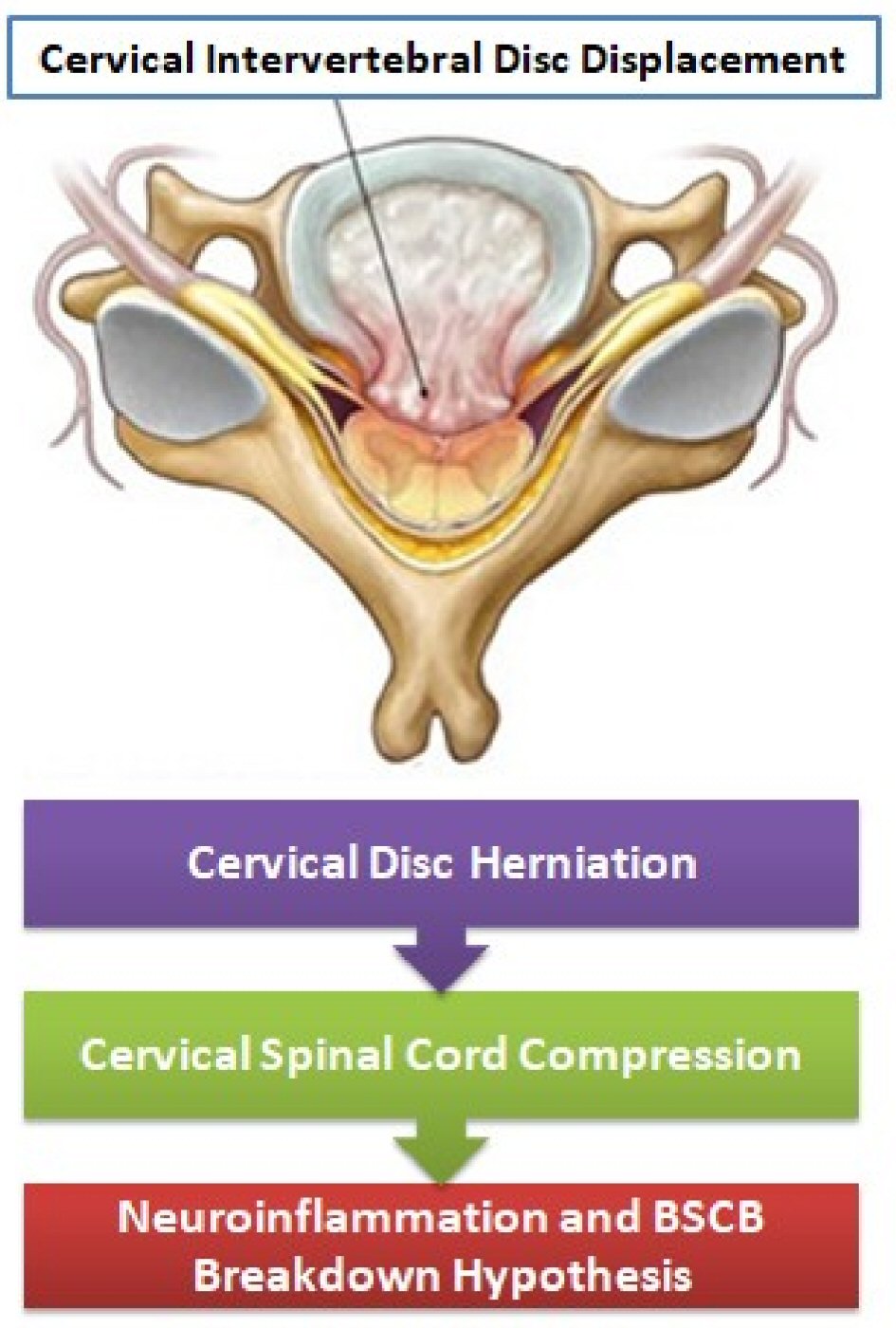
Figure 1. The BSCB breakdown hypothesis with neuroinflammation in MS patients after cervical spinal cord compression in CIDD. BSCB: blood-spinal cord barrier.
| Journal of Neurology Research, ISSN 1923-2845 print, 1923-2853 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Neurol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.neurores.org |
Short Communication
Volume 9, Number 3, June 2019, pages 35-38
Cervical Intervertebral Disc Displacement in Multiple Sclerosis Patients: A Possible Trigger for the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis?
Figure

Table
| Main author | Title | Journal |
|---|---|---|
| Xydis VG et al [11] | The association between multiple sclerosis and spondylosis: When and why | European Journal of Radiology |
| Russi AE et al [12] | The meninges: new therapeutic targets for multiple sclerosis | Translation Research |
| Uchida Y et al [13] | Involvement of claudin-11 in disruption of blood-brain, -spinal cord, and -arachnoid barriers in multiple sclerosis | Molecular Neurobiology |
| Aube B et al [14] | Neutrophils mediate blood-spinal cord barrier disruption in demyelinating neuroinflammatory diseases | The Journal of Immunology |
| Spencer JI et al [15] | Vascular pathology in multiple sclerosis: reframing pathogenesis around the blood-brain barrier | Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry |