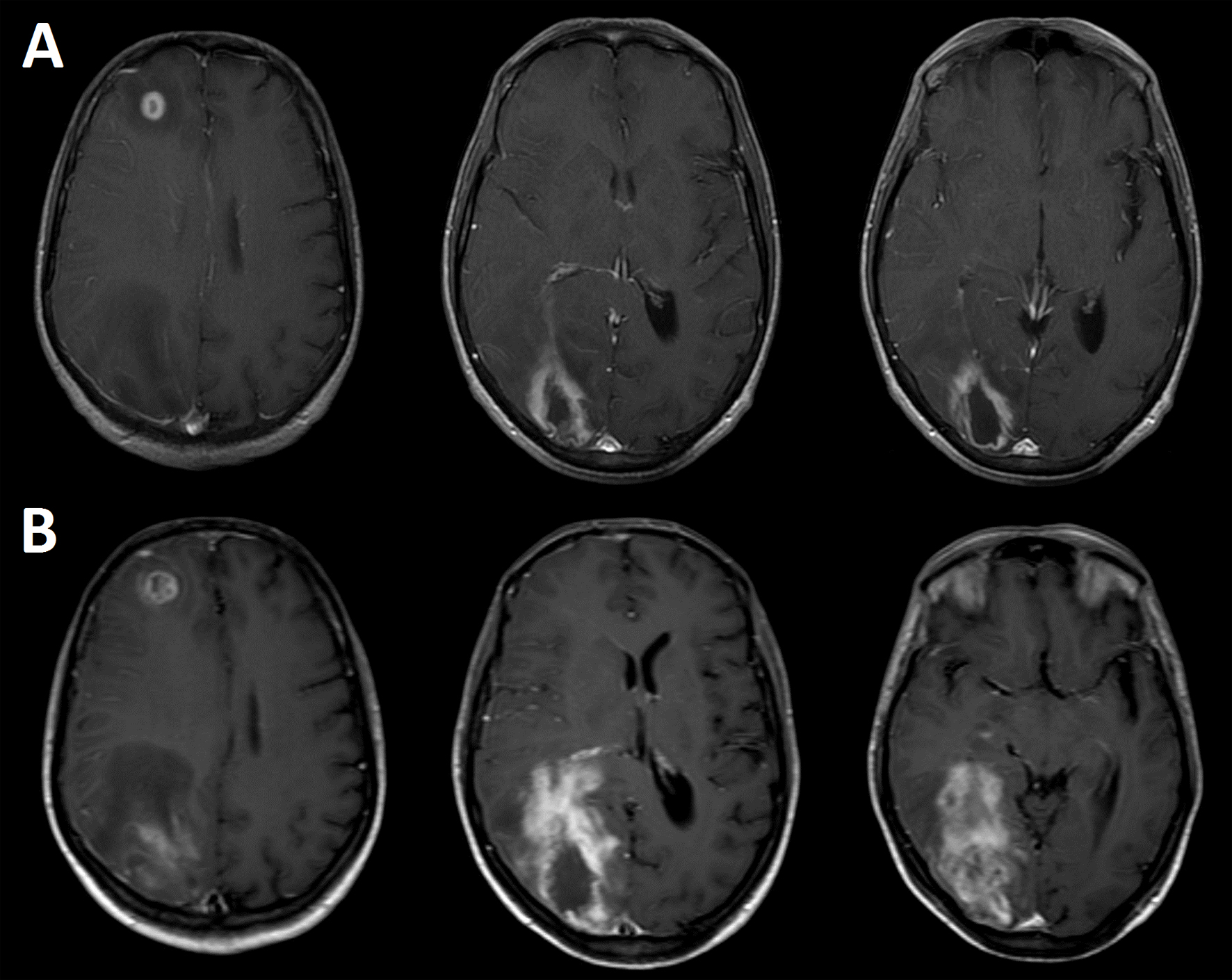
Figure 1. Contrast-enhanced (Gd-DTPA) axial brain T1-weighted images showing two cerebral lesions at the time of hospitalization (A), and 12 days after starting the anti-toxoplasmosis therapy (B). The images were acquired in a Philips Intera 1.5 T scanner with a standard quadrature head coil.
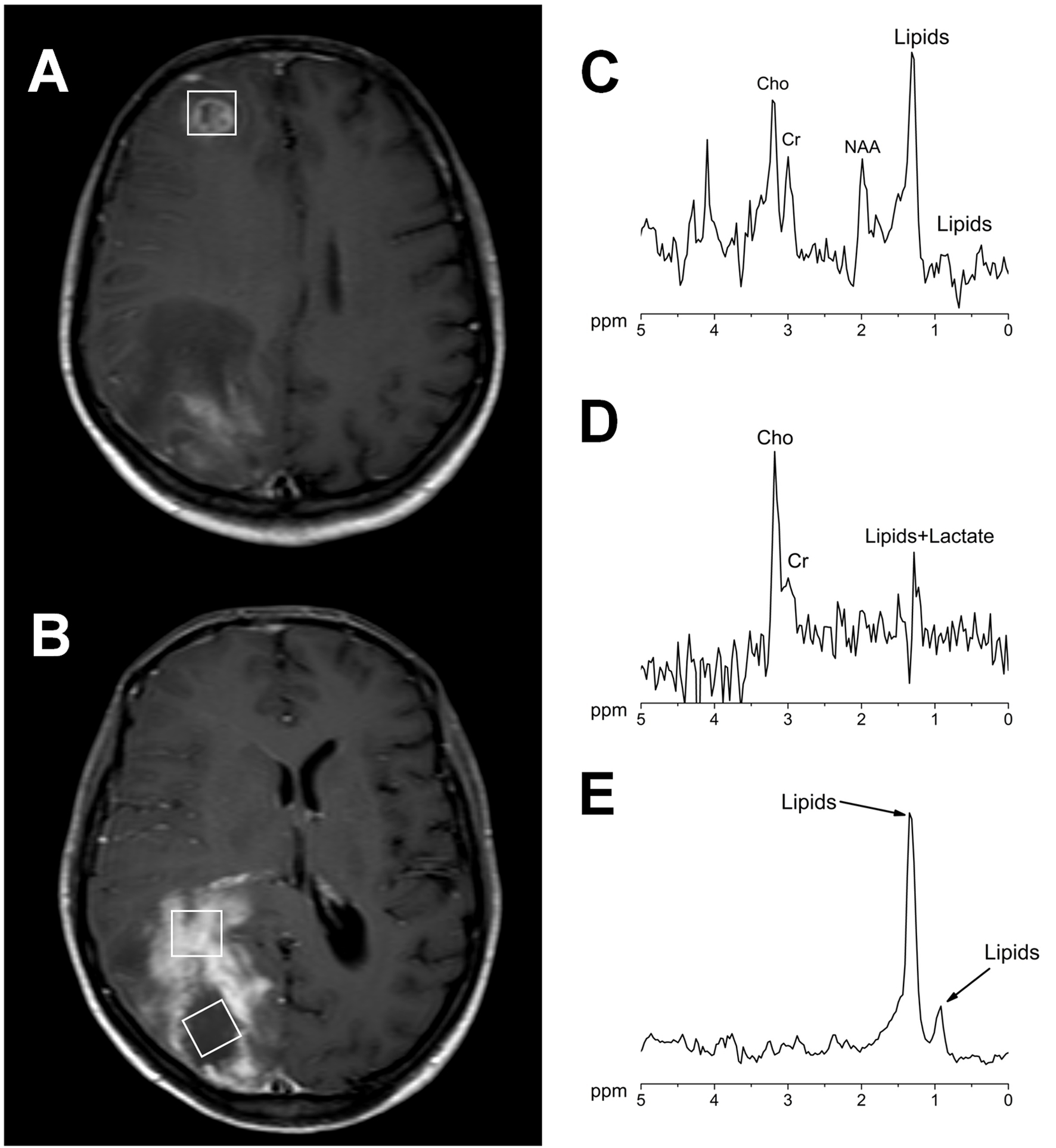
Figure 2. Contrast-enhanced axial brain T1-weighted images showing the voxel position in the measurement of both lesions (A, B). 1H MR spectra acquired at 144 ms echo time from the right frontal lesion (C), the occipital lesion in the contrast agent-enhancement area (D) and in the necrotic area (E). All the measurements were performed before the contrast agent injection in a Philips Intera 1.5 T with a standard quadrature head coil (PRESS/2000/144/128; Sequence/TR/TE/averages).
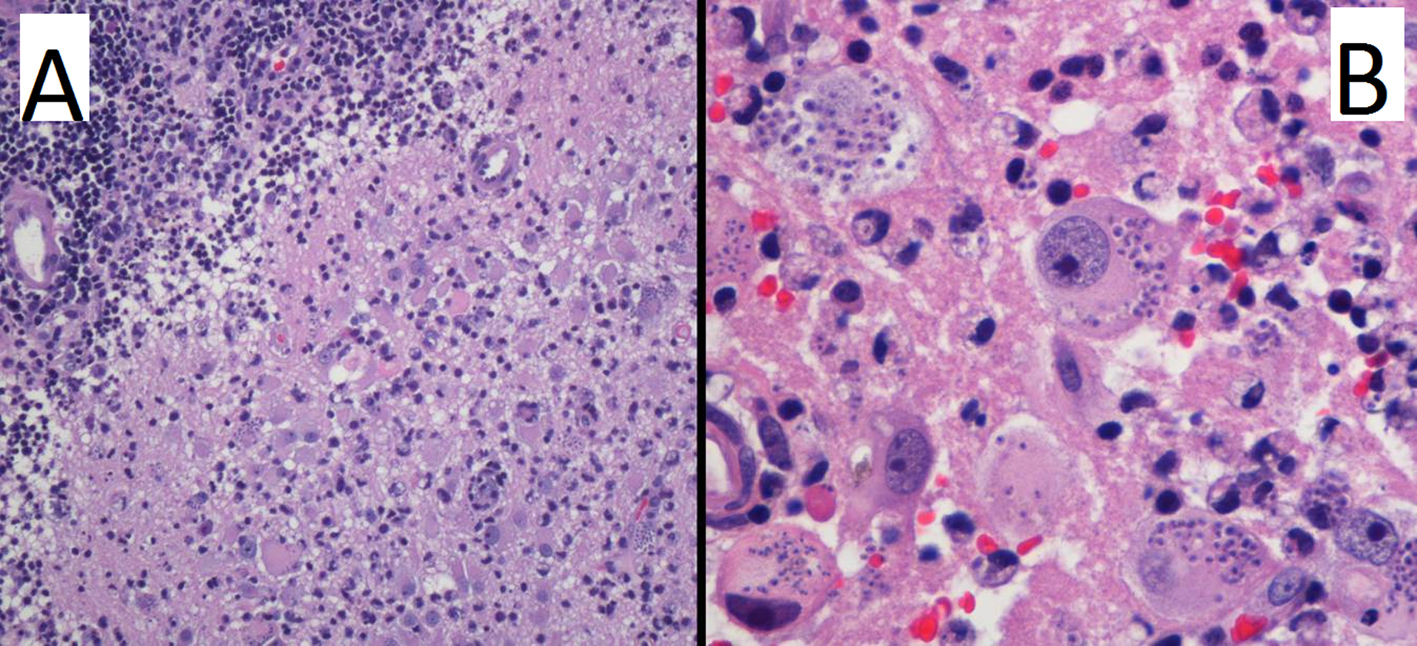
Figure 3. Hematoxylin and eosin stain at low (A) and high (B) power field. Images reveal brain parenchyma with necrosis and chronic inflammation (A), with the presence of lymphocytes and macrophages with intracytoplasmic parasites (B).


